Read eBook on Lokayatan app
Based on the New Education Policy.
*By purchasing you agree to the Terms & Conditions
CHAPTER – 1
INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING
Glimpse of Chapter
- Introduction
- Book-Keeping
- Meaning of Book-Keeping
- Definition of Book-Keeping
- Objectives of Book-Keeping
- Introduction of Accounting
- Meaning of Accounting
- Definition of Accounting
- Objectives of Accounting
- Importance of Accounting
- Functions of Accounting
- Advantages of Accounting
- Limitations of Accounting
- Bases of Accounting – cash basis and accrual basis
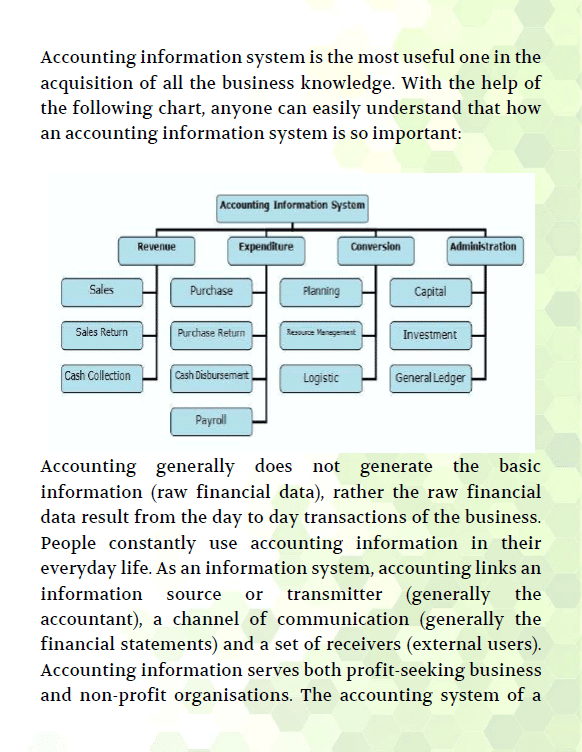
- Accounting as an information system
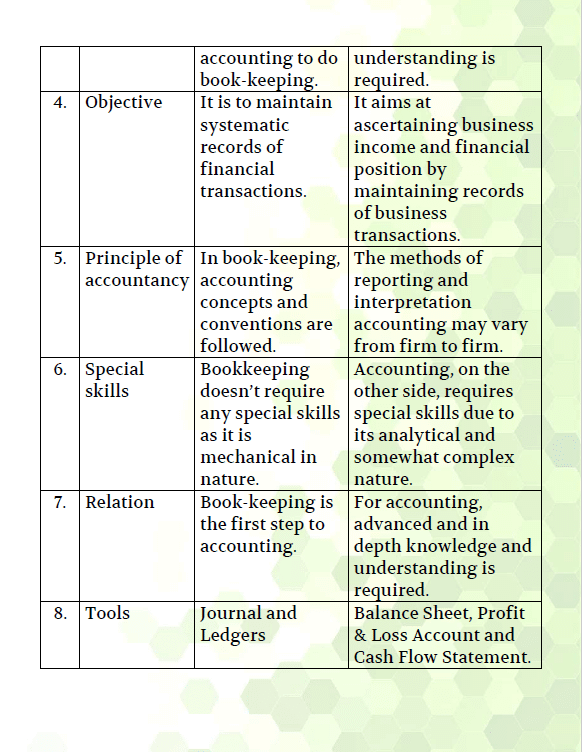
- Difference between Book Keeping, Accountancy and Accounting
- Exercise
1.0 Introduction
In all activities (whether business activities or non-business activities) and in all organizations (whether business organizations like a manufacturing entity or trading entity or non-business organizations like schools, colleges, hospitals, libraries, clubs, temples, political parties) which require money and other economic resources, accounting is required to account for these resources. In other words, wherever money is involved, accounting is required to account for it. Accounting is often called the language of business. The basic function of any language is to serve as a means of communication. Accounting also serves this function.
1.1 Book-Keeping
1.1.1 Meaning of Book-Keeping
Book-keeping includes recording of journal, posting in ledgers and balancing of accounts. All the records before the preparation of trail balance is the whole subject matter of book-keeping. Thus, book-keeping many be defined as the science and art of recording transactions in money or money’s worth so accurately and systematically, in a certain set of books, regularly that the true state of businessman’s affairs can be correctly ascertained. Here it is important to note that only those transactions related to business are recorded which can be expressed in terms of money.
1.1.2 Definitions of Book-Keeping
According to A. H. Rosenkamph – “Book-keeping is the art of recording business transactions in a systematic manner.” According to R. N. Carter – “Book-keeping is the science and art of correctly recording in books of account all those business transactions that result in the transfer of money or money’s worth.”
1.1.3 Objectives of Book-Keeping
1. Amendment of business laws, provision of licenses, assessment of taxes etc., are based on records.
2. Book-keeping provides a permanent record of each transactions.
3. Entries related to incomes and expenditures of a concern facilitate to know the profit and loss for a given period.
4. It enables to prepare a list of customers and suppliers to ascertain the amount to be received or paid.
5. It is a method that gives opportunities to review the business policies in the light of past records.
6. Soundness of a firm can be assessed from the records of assets and abilities on a particular date.
Overview & Preview
| Book Type: | eBook, PDF (815 pages), 44 Chapters |
|---|---|
| Language: | English |
| ISBN: | 978-93-92308-02-4 |
This book is covering the complete syllabus of Financial Accounting. It is the only book of its kind which is student-friendly, teaching convenient, and exam-oriented at the same time. The main purpose of this book is to enable the student to write the correct, logical, relevant, coherent, well proportioned, and impressive answers to the questions asked in the examination.
The book has been written in very simple and understandable language along with the appropriate examples, diagrams, and other student-friendly concepts. Not only this book covers the long answer-type questions but also the short answer-type questions. Both of the question types are organized in the unit-wise syllabus.
Sample Pages
APPBOOK
Lokayatan publication has come up with this innovative idea to make the learning process even more fun and engaging for learners.
Stay
CONNECTED